URL inspection feature in the Google Search Console is an important that you must know how to use in the right way.

Developing a world-class website requires time, money, creativity, and effort. Yet all of this will go in vain if your website–or some of its important pages–do not show up on Google search.
As more than 93% of all internet activity begins with a search, your webpage must be indexed. This is of utmost necessity if you have created a new page or published a new blog.
In order to get your web pages indexed, Googlebot must crawl your website, and only after it ensures that your website meets the guidelines for indexing, does it index your page.
Why URL Inspection Tool Matters
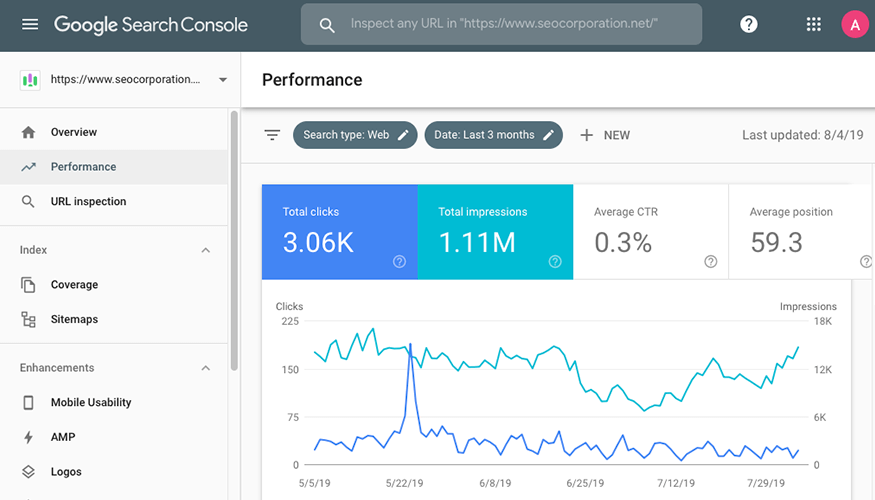
In June 2018, Google came up with a URL Inspection Tool as part of its Search Console. Using this tool you can get detailed information about crawl, index and serving information regarding your pages by simply entering its URL.
In addition, if your page is not indexed, it tells you why making it easier for you to track down the issue and fix it.
With the help of this tool, your non-indexed pages will no longer remain a mystery and you can understand what went wrong.
What Tasks Does URL Inspection Tool Perform?
The main job of the URL Inspection Tool is to collate and provide information about Google’s indexed version of a particular page. The details could be related to the different indexing issues resulting from not following Google’s indexing guidelines properly or to AMP and structured data errors.
The list of tasks the tool performs 4 major tasks:
1. Providing the Current Index Status of a URL
This helps you see whether your page is indexed or not. If not, then why?
2. Inspecting a Live URL
This relates to checking whether the URL of your website is indexable or not.
3. Requesting a URL to be Crawled
This feature allows you to request Googlebot to crawl or re-crawl.
4. Viewing a Rendered Version
This allows you to see how Googlebot views your page.
Apart from this, the inspection tool also allows you to see page code, list of resources, and a few other information related to the link. We will discuss about the above status one by one.
How to See the Current Index Status of a URL
Very simple! Click “URL Inspection” in the search console and enter the URL you want information about. Make sure the URL you are inspecting is your own property as anything outside the current property will not be inspected.
You can also get information about duplicate pages if any. The tool also helps you inspect both AMP and non-AMP URLs. However, there is an external limit to the inspection requests you can raise for a particular property.
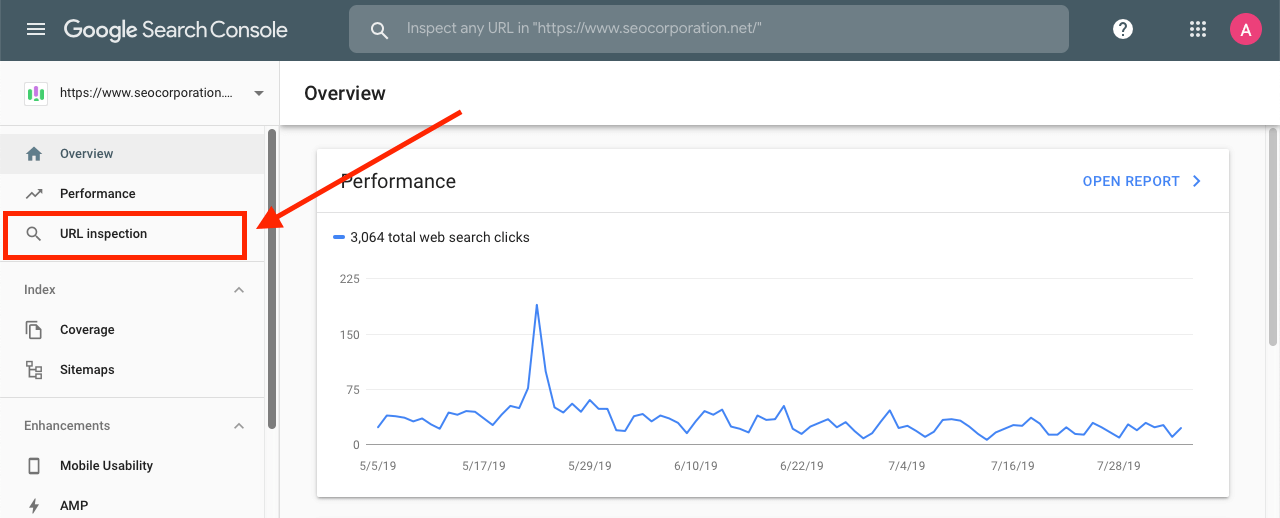

How to Interpret the Result
The inspection tool gives you a peek into the URL of the page.
There can be 4 possible outcomes:
1. URL is on Google
If this is the case, your URL is indexed and can show up in search results. This type of URL has no issues pertaining to structured data, AMP pages, etc. and you can relax as there is nothing much to do for you in this scenario.
However, The URL Inspection tool doesn’t consider manual actions, content removals, or temporarily blocked URLs and your content may not appear in search result despite the URL is on Google.
How to Fix
There is not much you need to do in this scenario. However, you can still go in-depth and find out what else Google knows about your page by scanning the index coverage and enhancement sections.
In order to see if your URL is still blocked, visit the “Remove URLs tool” or search for your URL on Google.
2. URL is on Google, with Issues
In this scenario, your page will show up on Google search as it is indexed, but it might be prevented from appearing with enhancements applied to the page. The reason for this problem could be an issue with structured data or an AMP page issue
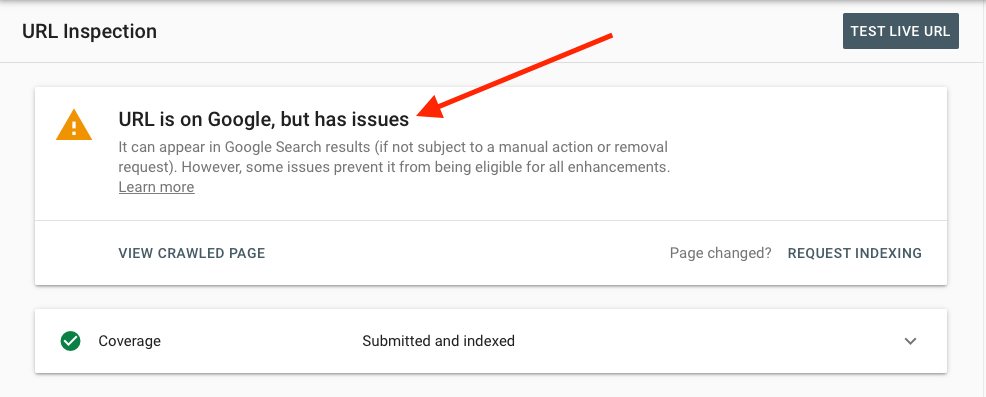

Image Credit: Google
How to Fix
The inspection tool report also provides warnings and errors. Read them carefully and try to fix the issue accordingly.
3. URL is not on Google (Indexing Issues)
Since the page is not indexed, your page doesn’t appear in the search results. There is a critical error that has happened which is preventing the URL from being indexed.
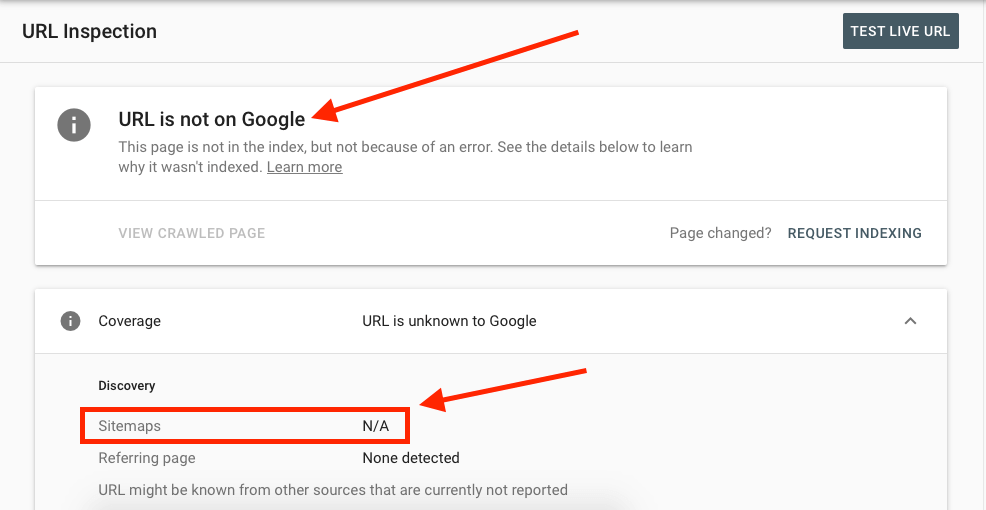

Image Credit: Ahref
How to Fix
Indexing errors could be of many types.
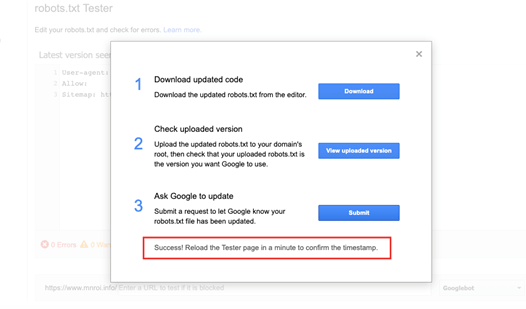
If Submitted URL is blocked by robots.txt: Try testing your page using the robots.txt tester.

Submitted URL marked ‘noindex’: If you want this page to be indexed, you must remove the tag or HTTP header.
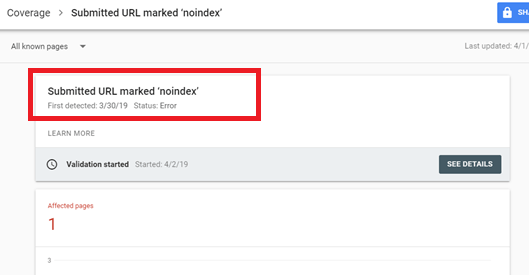

Image Credit: Google
Submitted URL seems to be a Soft 404: You submitted this page for indexing, but the server returned what seems to be a soft 404.

Image Credit: Google
4. URL is not on Google (Deliberate Case)
Apart from indexing issues, there is also the possibility that you don’t want your page indexed. It could be the case that your page is password protected or a nonindex directive.
Another reason could be that the current page is an alternate version of the canonical page (with the original one being already indexed).
How to Fix
Check the possible reasons as shown in the screenshot above and try to fix the problem.
How to Inspect a Live URL
Inspection of a live URL is done to check whether the URL of the property you own is capable of being indexed or not. This comes in handy when you want to test some changes to the given page against one that is already indexed.
Here are the steps to test a live URL for potential errors:
- Start with inspecting the indexed URL as discussed in the above section. It is important to note that this page must be accessible from the internet without adding any login information.
- Click on “Test Live URL” on the index results page.
- You can also see the details of the page by selecting “View Crawled Page.” Google has put a daily limit for inspections per property.
How to Interpret the Results
The inspection can only have 3 possible outcomes as discussed below:
1. URL is on Google
If the URL is not blocked, it means it does not have any detectable errors. However, this does not mean it will always show up on Google search. This can only be guaranteed if the URL follows the guidelines related to security and quality.
How to Fix
If you find out that the indexed page is different from the current page, then you can select the appropriate button to request indexing.
2. URL is on Google, with Issues
Same as explained above; the issues could be related to AMP or structured data. Mere presence on Google does not necessitate that your URL will show up on the search results.
How to Fix
Follow the error message and warnings to fix your problem.
3. URL is not on Google
This means that the URL cannot appear on Google search due to some critical issues.
How to Fix
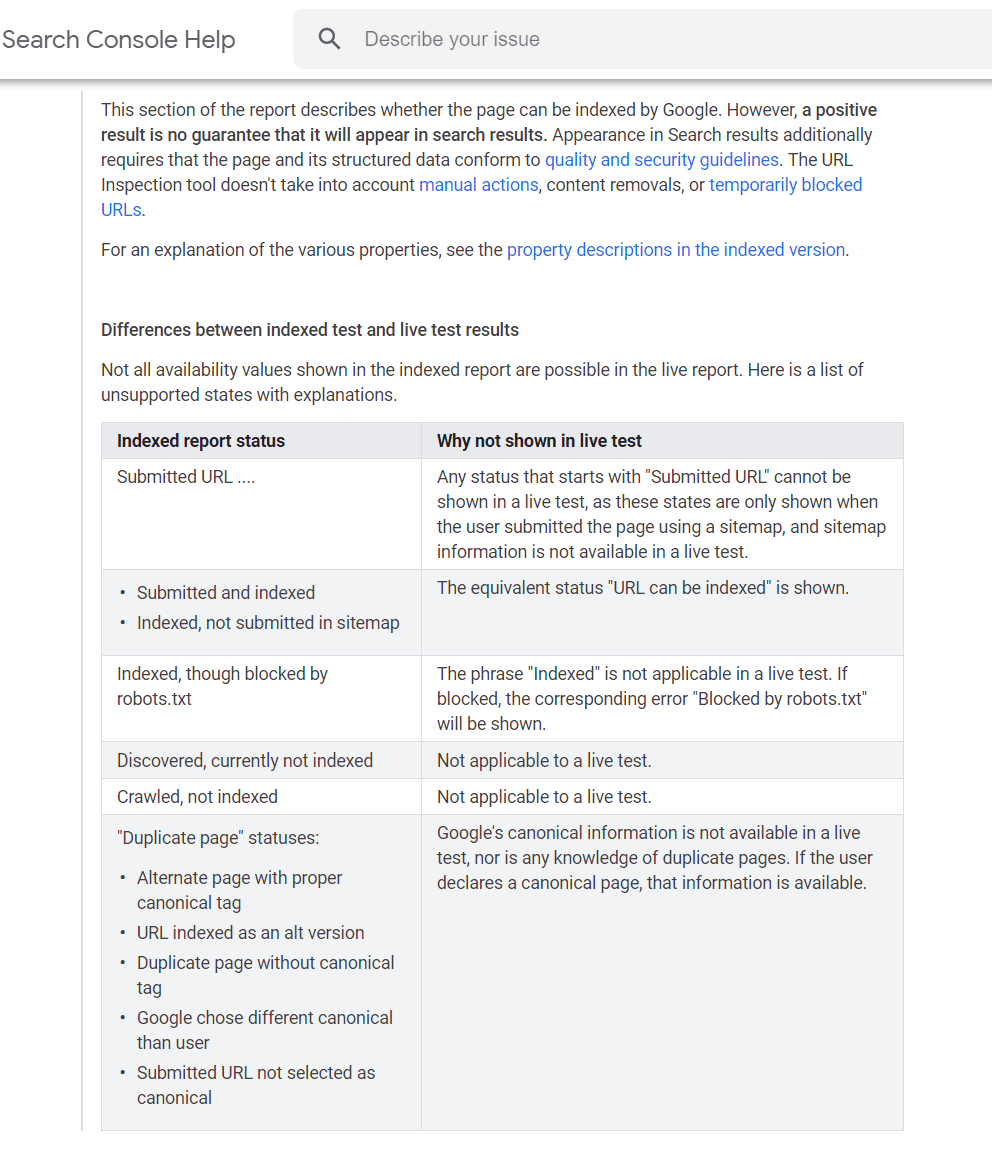
It is important to note here that a positive result does not necessitate that your page will appear in the search results. In fact, there is a difference between indexed results and live test results.
Please refer to the section below to see all the unsupported states with clear explanations on each of them.

How to View a Rendered Page
Interestingly, you can view the screenshot of a rendered page as Googlebot sees it.
This helps you ensure that all the elements of the page are available and appear before the users as you want them to appear.
It is important to note that the view of the rendered page is available only for live URL tests and not for the indexed URL.
However, if your page is hiding behind a firewall, then you can make it available and expose it to the inspection tool by using a tunnel.
The steps to view the rendered page are:
- Perform a live URL test
- Click “View Tested Page” to open additional available panels
- Select the “Screenshot” tab
How to Request (Re)Indexing
If any URL is not indexed then you can request re-indexing for your URL using this tool. Note that it generally takes 1-2 weeks for a page to get indexed. The tool allows you to check the status of indexing as well.
To conclude, the URL Inspection Tool is a worthy addition to Google’s Search Console.
It gives you an insight into what is wrong with your URL and also guides you on how to get it indexed so that it comes up in the search results.
By using this tool, you can increase the page visits for your website and help your business expand significantly.